Reactive Dyes Examples
Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
In a reactive dye, a chromophore (an atom or group whose presence is responsible for the colour of a compound) contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon.
Reactive Dyes | PPT

Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
Dye - Reactive, Synthetic, Colorfast: The first examples of reactive dyes utilized monoazo systems for bright yellow and red shades. Coupling aniline to H-acid gave the azo dye used in the first Procion Red (C.I. Reactive Red 1), and anthraquinone dyes were used to obtain bright blue shades.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
Different Types Of Reactive Dyes: Properties, Structures And Factors

Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
In a reactive dye, a chromophore (an atom or group whose presence is responsible for the colour of a compound) contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Reactive Dyes By Engr Aashiq
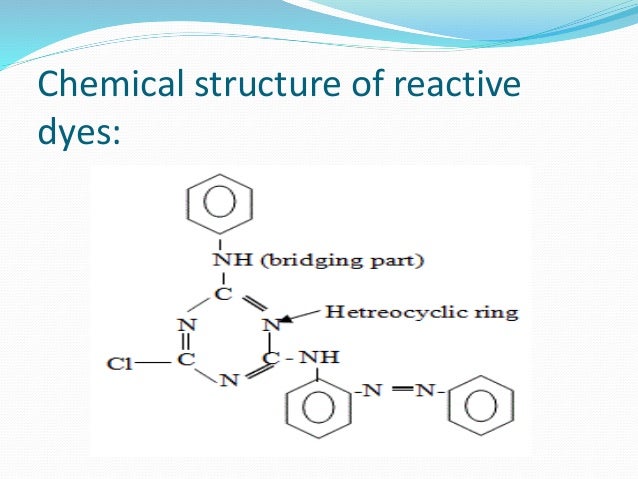
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
Chemical Structures Of Reactive Dyes. | Download Scientific Diagram

This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
Dye - Reactive, Synthetic, Colorfast: The first examples of reactive dyes utilized monoazo systems for bright yellow and red shades. Coupling aniline to H-acid gave the azo dye used in the first Procion Red (C.I. Reactive Red 1), and anthraquinone dyes were used to obtain bright blue shades.
Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Fundamentals Of Fibre Reactive Dyes » School Of SweetGeorgia

Dye - Reactive, Synthetic, Colorfast: The first examples of reactive dyes utilized monoazo systems for bright yellow and red shades. Coupling aniline to H-acid gave the azo dye used in the first Procion Red (C.I. Reactive Red 1), and anthraquinone dyes were used to obtain bright blue shades.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Definition: In a reactive dye a chromospheres contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the bonding that occurs during dyeing. Various types of reactive dyes are most commonly used in dyeing of cellulose like cotton or flax, but also wool is dye able with reactive dyes.
This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
Reactive Dyes: Types, Classification & Structure | Meghmani

Explore the science behind reactive dyes, including their covalent bonding mechanisms, structural classifications, synthesis methods, and industrial applications in textiles, biotechnology, and paper. Learn how Alfa Chemistry supports sustainable innovations and custom solutions in reactive dye technology.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
Definition: In a reactive dye a chromospheres contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the bonding that occurs during dyeing. Various types of reactive dyes are most commonly used in dyeing of cellulose like cotton or flax, but also wool is dye able with reactive dyes.
In a reactive dye, a chromophore (an atom or group whose presence is responsible for the colour of a compound) contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon.
The Chemical Structure Of Reactive Dyes. | Download Scientific Diagram

Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Explore the science behind reactive dyes, including their covalent bonding mechanisms, structural classifications, synthesis methods, and industrial applications in textiles, biotechnology, and paper. Learn how Alfa Chemistry supports sustainable innovations and custom solutions in reactive dye technology.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
Reactive Dye || Reactive Dye Features || Reactive Dye Classification | Textile Study Center
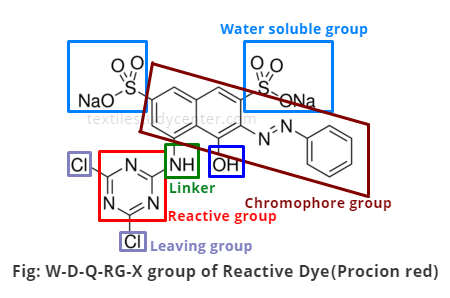
Dye - Reactive, Synthetic, Colorfast: The first examples of reactive dyes utilized monoazo systems for bright yellow and red shades. Coupling aniline to H-acid gave the azo dye used in the first Procion Red (C.I. Reactive Red 1), and anthraquinone dyes were used to obtain bright blue shades.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
In a reactive dye, a chromophore (an atom or group whose presence is responsible for the colour of a compound) contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon.
Definition: In a reactive dye a chromospheres contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the bonding that occurs during dyeing. Various types of reactive dyes are most commonly used in dyeing of cellulose like cotton or flax, but also wool is dye able with reactive dyes.
Reactive Dyes And Its Mechanism
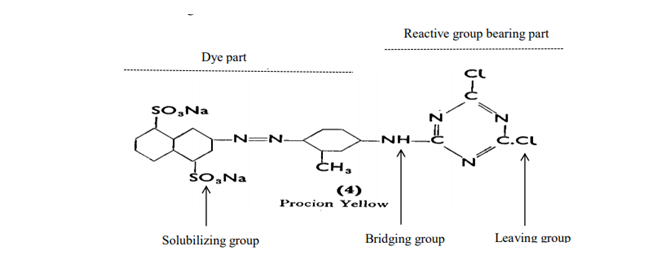
Explore the science behind reactive dyes, including their covalent bonding mechanisms, structural classifications, synthesis methods, and industrial applications in textiles, biotechnology, and paper. Learn how Alfa Chemistry supports sustainable innovations and custom solutions in reactive dye technology.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Definition: In a reactive dye a chromospheres contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the bonding that occurs during dyeing. Various types of reactive dyes are most commonly used in dyeing of cellulose like cotton or flax, but also wool is dye able with reactive dyes.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
Reactive Dyes | PPT

This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
Dye - Reactive, Synthetic, Colorfast: The first examples of reactive dyes utilized monoazo systems for bright yellow and red shades. Coupling aniline to H-acid gave the azo dye used in the first Procion Red (C.I. Reactive Red 1), and anthraquinone dyes were used to obtain bright blue shades.
Molecular Structures Of Reactive Dyes. | Download Scientific Diagram

Definition: In a reactive dye a chromospheres contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the bonding that occurs during dyeing. Various types of reactive dyes are most commonly used in dyeing of cellulose like cotton or flax, but also wool is dye able with reactive dyes.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
PPT - Dye Classification Dyeing Processes PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID:6788546

In a reactive dye, a chromophore (an atom or group whose presence is responsible for the colour of a compound) contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
Dyeing Fabric With Fiber Reactive Dyes Beginner's Guide - FiberArtsy.com

Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Explore the science behind reactive dyes, including their covalent bonding mechanisms, structural classifications, synthesis methods, and industrial applications in textiles, biotechnology, and paper. Learn how Alfa Chemistry supports sustainable innovations and custom solutions in reactive dye technology.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
Reactivity Of Reactive Dyes?

This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
Reactive Dyes In Dyeing | DOCX | Chemistry | Science

Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.
Reactive dyes are very commonly used in the textile industry on different materials such as wool, silk, and cotton. Different popular applications of reactive dyes include exhaust dyeing, discharge printing, and inkjet printing.
Definition: In a reactive dye a chromospheres contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the bonding that occurs during dyeing. Various types of reactive dyes are most commonly used in dyeing of cellulose like cotton or flax, but also wool is dye able with reactive dyes.
Learn everything you need to know about reactive dyes how to use them to get started with brightening up your fabrics.
In a reactive dye, a chromophore (an atom or group whose presence is responsible for the colour of a compound) contains a substituent that reacts with the substrate. Reactive dyes have good fastness properties owing to the covalent bonding that occurs during dyeing. Reactive dyeing is the most important method for coloring cellulose fibers. Reactive dyes can also be applied on wool and nylon.
This article covers reactive dye chemical structure, types, classifications based on types of reactions, and some tips when using reactive dyes.
This article delves into the world of reactive dyes, exploring their chemistry, principles of dyeing, different types, application processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages they bring. Additionally, we will explore the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns associated with reactive dyes.
Reactive dyes are the most widely used dyestuff for dyeing cellulosic materials. The reason behind its dominance is its excellent fastness properties.
Explore the science behind reactive dyes, including their covalent bonding mechanisms, structural classifications, synthesis methods, and industrial applications in textiles, biotechnology, and paper. Learn how Alfa Chemistry supports sustainable innovations and custom solutions in reactive dye technology.
Dye - Reactive, Synthetic, Colorfast: The first examples of reactive dyes utilized monoazo systems for bright yellow and red shades. Coupling aniline to H-acid gave the azo dye used in the first Procion Red (C.I. Reactive Red 1), and anthraquinone dyes were used to obtain bright blue shades.
Reactive dyes is a cationic dyes. Cationic dyes this term express that the reactive portion of the dye holds a positive charge while reacting with the substrate.